Image to Image
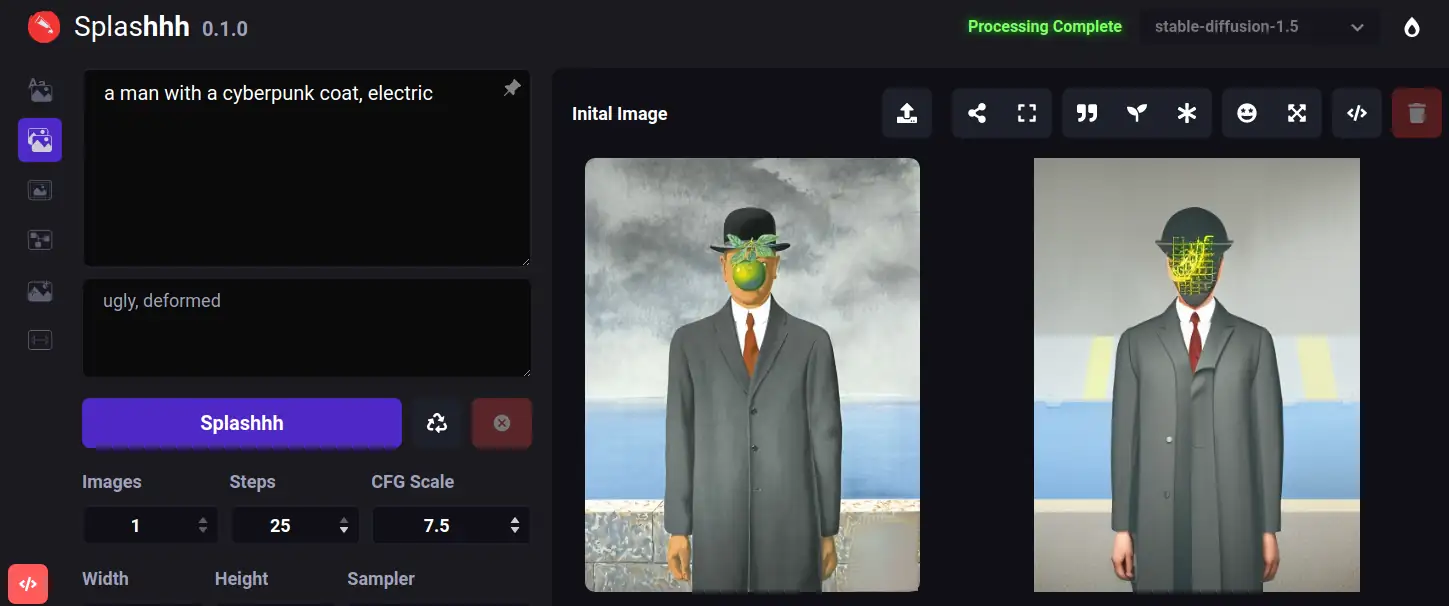
Image to image using an AI generative model
The Image-to-Image feature is a type of generative model that takes an input image and generates an output image that has been modified in some way. It is often used for tasks such as image colorization, style transfer, and image inpainting.
The Image-to-Image model works by using a deep neural network to learn a mapping function between the input and output images. The network is trained on a dataset of input-output image pairs, where the output images are known and correspond to a desired modification of the input images. During training, the network adjusts its parameters to minimize the difference between the generated output images and the ground truth output images.
One popular type of Image-to-Image model is the Conditional Generative Adversarial Network (CGAN), which consists of two networks: a generator and a discriminator. The generator takes as input the input image and generates an output image, while the discriminator takes as input both the input and output images and tries to determine whether the output image is real or fake.
During training, the generator and discriminator networks play a game in which the generator tries to generate realistic output images that can fool the discriminator, while the discriminator tries to correctly distinguish between real and fake output images. This process is repeated until the generator learns to generate output images that are indistinguishable from real output images.
Once the Image-to-Image model has been trained, it can be used to modify input images in a variety of ways. For example, it can be used to colorize black and white images, by taking a grayscale input image and generating a colorized output image that matches the input. It can also be used to transfer the style of one image to another, by taking a content image and a style image and generating an output image that combines the content of the content image with the style of the style image.
Image to image using the Stable Diffusion ML model
Stable Diffusion is a generative model that can be used for Image-to-Image tasks. It is based on modeling the diffusion process of pixels in an image over time, using a deep neural network to parameterize the diffusion process.
The model is trained on a dataset of input-output image pairs to use Stable Diffusion for Image-to-Image tasks. During training, the input image is first passed through an encoder network, which maps it to a lower-dimensional latent space. The latent representation is then fed into the diffusion process, which gradually modifies the pixel values of the input image to produce the output image. The diffusion process is parameterized by a deep neural network, optimized to predict the next pixel value given the current pixel value and a noise term. The noise term is added at each diffusion process step to introduce randomness and ensure that the generated output images are diverse.
Once the diffusion process is complete, the output image is passed through a decoder network, which maps it back to the original image space. The entire model is trained end-to-end using a loss function that encourages the generated output images to be as close as possible to the ground truth output images.
The Image-to-Image feature of Stable Diffusion can be used for various tasks, such as image denoising, super-resolution, and style transfer. To use the model for a specific task, the architecture of the encoder and decoder networks may need to be modified, depending on the characteristics of the input and output images.